Monthly Archives: September 2017
Prime Sieve in Java
A very concise prime sieve implementation in Java.
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac PrimeSieve.java
* Execution: java -Xmx1100m PrimeSieve n
*
* Computes the number of primes less than or equal to n using
* the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
*
* % java PrimeSieve 25
* The number of primes <= 25 is 9
*
* % java PrimeSieve 100
* The number of primes <= 100 is 25
*
* % java -Xmx100m PrimeSieve 100000000
* The number of primes <= 100000000 is 5761455
*
* % java PrimeSieve -Xmx1100m 1000000000
* The number of primes <= 1000000000 is 50847534
*
*
* The 110MB and 1100MB is the amount of memory you want to allocate
* to the program. If your computer has less, make this number smaller,
* but it may prevent you from solving the problem for very large
* values of n.
*
*
* n Primes <= n
* ---------------------------------
* 10 4
* 100 25
* 1,000 168
* 10,000 1,229
* 100,000 9,592
* 1,000,000 78,498
* 10,000,000 664,579
* 100,000,000 5,761,455
* 1,000,000,000 50,847,534
*
******************************************************************************/
public class PrimeSieve {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
// initially assume all integers are prime
boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[n+1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
isPrime[i] = true;
}
// mark non-primes <= n using Sieve of Eratosthenes
for (int factor = 2; factor*factor <= n; factor++) {
// if factor is prime, then mark multiples of factor as nonprime
// suffices to consider mutiples factor, factor+1, ..., n/factor
if (isPrime[factor]) {
for (int j = factor; factor*j <= n; j++) {
isPrime[factor*j] = false;
}
}
}
// count primes
int primes = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (isPrime[i]) primes++;
}
System.out.println("The number of primes <= " + n + " is " + primes);
}
}
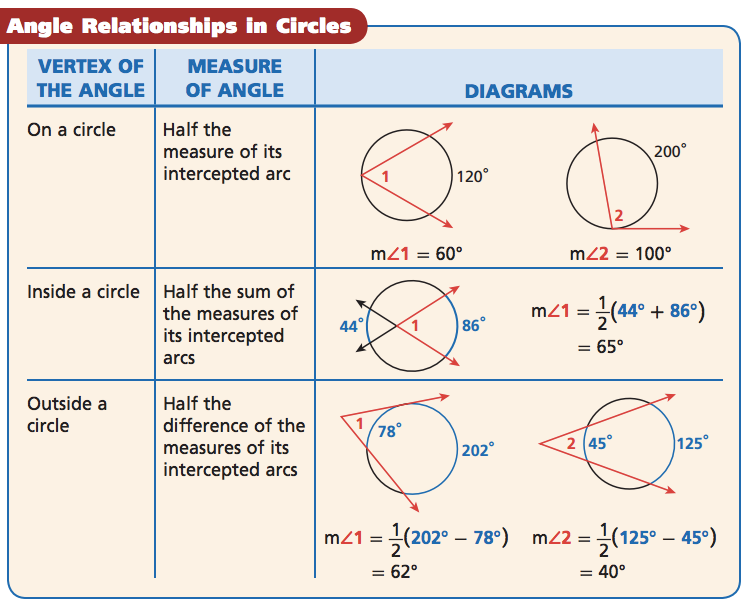
Circle-Angle Formulas
Merge Sort in Python
def merge(a,b):
""" Function to merge two arrays """
c = []
while len(a) != 0 and len(b) != 0:
if a[0] < b[0]:
c.append(a[0])
a.remove(a[0])
else:
c.append(b[0])
b.remove(b[0])
if len(a) == 0:
c += b
else:
c += a
return c
# Code for merge sort
def mergesort(x):
""" Function to sort an array using merge sort algorithm """
if len(x) == 0 or len(x) == 1:
return x
else:
middle = round(len(x)/2)
a = mergesort(x[:middle])
b = mergesort(x[middle:])
return merge(a,b)